Spring Lifecycle
编辑
为什么需要了解 Spring 生命周期
Spring 的核心内容之一就是 Bean 的生命周期, 而这部分逻辑大部分内容都封装在 refresh 中, 外部看上去风平浪静,其实内部则是一片惊涛骇浪. Spring Boot更是封装了 Spring,遵循约定大于配置,加上自动装配的机制, 很多时候我们只要引用了一个依赖,几乎是零配置就能完成一个功能的装配。
了解 Spring Bean的生命周期的同时也是在了解 Spring 的一些拓展点, 加深对 Spring 的理解, 有助于我们合理正确的利用拓展点去实现一些中间件或者横切业务逻辑的实现. 为什么需要合理正确的使用这些拓展点, 不是能用就行了吗? 确实大部分时候, 在当下的时候能用就行, 但是否想过会不会为以后埋下坑或者已经欠了技术债务了呢? 比如:
在过早的时机启动了一些组件导致部分 Bean 没有被 BeanPostProcessor 增强
本该可以异步启动组件却在 Spring Bean 初始化阶段启动
不按标准化的步骤封装一些 starter 组件
正如 Docker 的最佳实践是一个实例只有一个进程, 但不影响在里面起多个进程的做法, Spring 依赖注入的最佳实践是构造器注入, 但并不影响使用 @Autowired 进行循环依赖注入(A依赖B, B依赖A). 但类似这种非标准化的做法往往会在某个阶段出现问题, 拿前面两个 case 来说, Docker 多进程违反单一职责导致优雅关机失败, 因为 Docker 默认只会通知 PID 为 1 的进程进行关机操作; 而 Spring 循环依赖解决已经在 Spring Boot 2.6 的版本默认关闭, 虽然可以通过配置进行开启, 但谁知道哪天 Spring 会直接不支持循环依赖了呢?
Spring Bean 生命周期简约版
Spring Bean的生命周期只有这四个阶段。实例化对应构造方法,属性赋值对应setter方法的注入,初始化和销毁是用户能自定义扩展的两个阶段。
实例化 -> 属性赋值 -> 初始化 -> 销毁
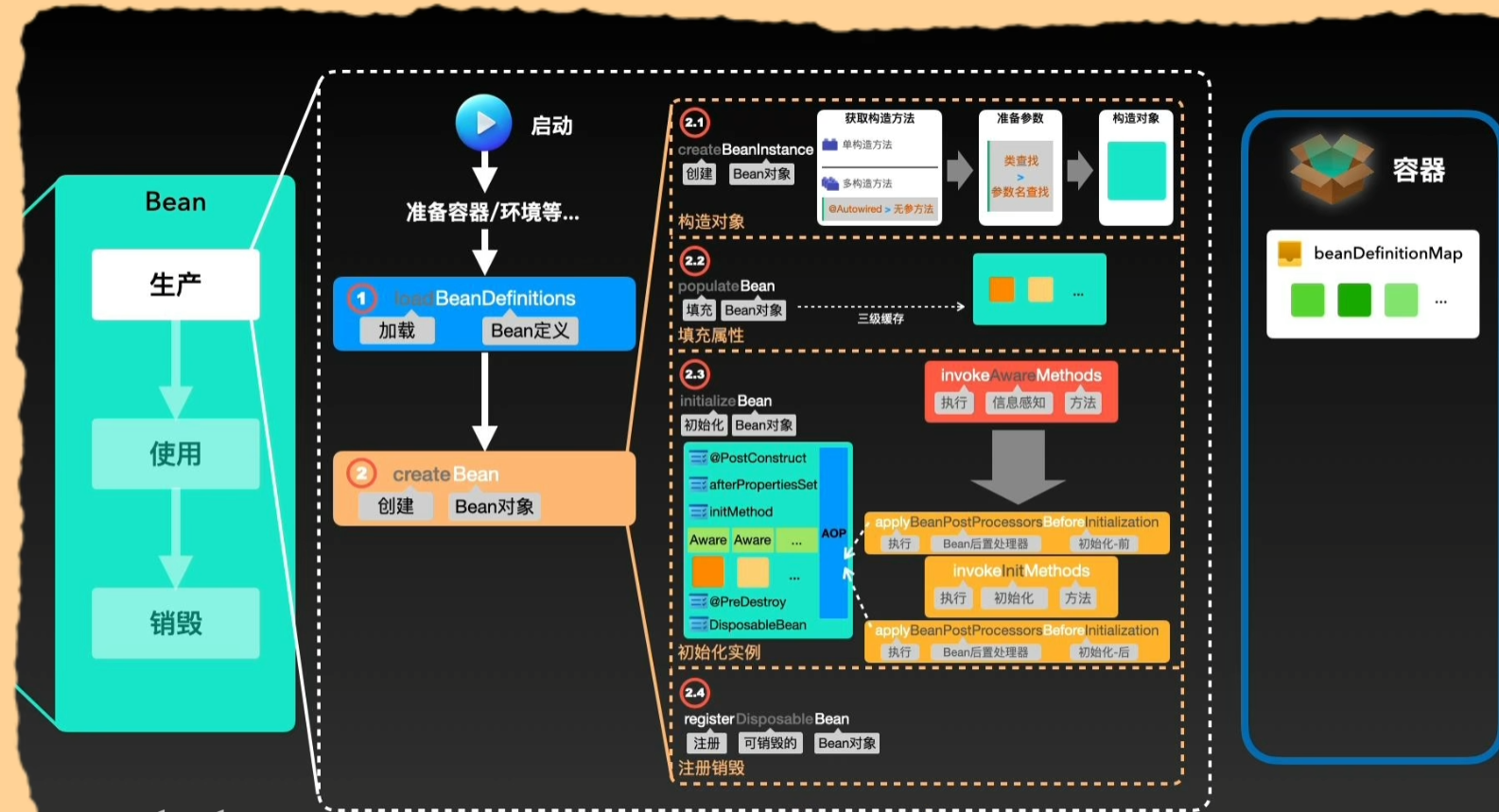
实例化
通过反射调用构造器构造 Bean
不建议多个构造器
属性赋值/依赖注入, 三级缓存
@Autowiredsetter 方法
初始化
*Aware接口填充@PostConstructInitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet@Bean中定义的initMethod
所有 Bean 初始化后回调
SmartInitializingSingleton#afterSingletonsInstantiated销毁
@PreDestroyDisposableBean#destroy@Bean中定义的destroyMethod
相关源码在 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean:
// 忽略了无关代码
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 实例化阶段!
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 属性赋值阶段!
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化阶段!
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}而 Bean 的依赖注入, 初始化都依赖了一个重要的接口: BeanPostProcessor, 这也是一个常用的拓展点, 另外还有一个 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, 对应 Bean 的生命周期:
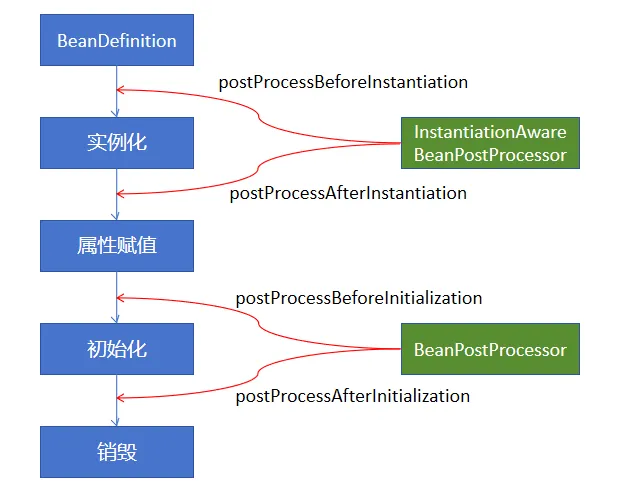
另外 BeanPostProcessor 其中一部分继承关系:
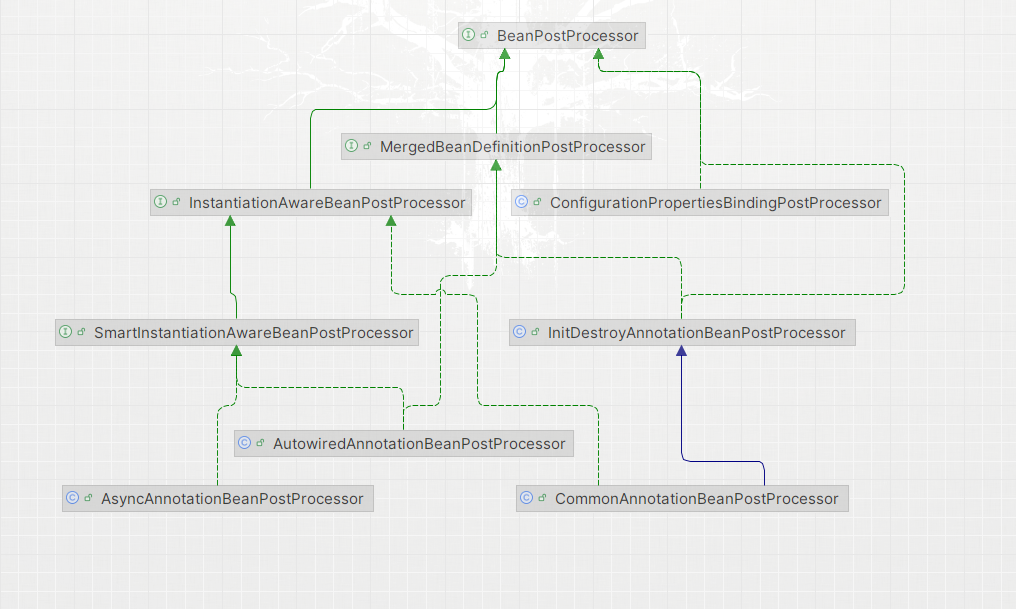
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理@Autowired, setter 等依赖注入InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理初始化/销毁方法AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理@Async注解, 生成异步代理对象ApplicationContextAwareProcessor: 处理大部分 Aware 接口注入对应资源, 比如ApplicationContextAware,EnvironmentAware除了
BeanNameAware,BeanClassLoaderAware以及BeanFactoryAware, 这几个 Aware 是在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeAwareMethods处理的.
ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor: 处理@ConfigurationProperties注解, 给配置类注入对应的 Properties
BeanPostProcessor有众多实现, 它们的顺序由PriorityOrdered以及Ordered接口决定.
PiorityOrdered是一等公民,首先被执行,PriorityOrdered公民之间通过接口返回值排序
Ordered是二等公民,然后执行,Ordered公民之间通过接口返回值排序
都没有实现是三等公民,最后执行
Spring 生命周期一图流
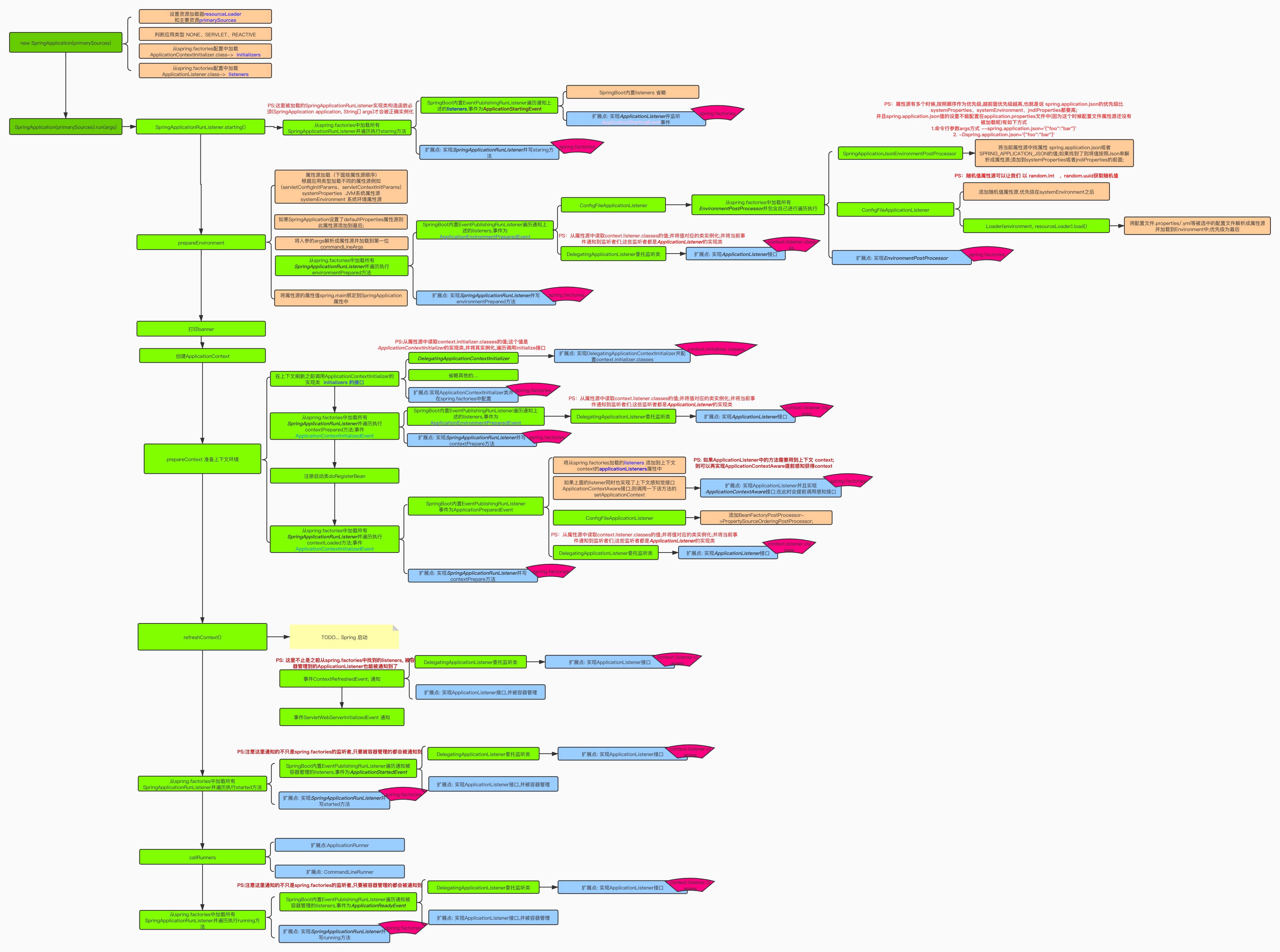
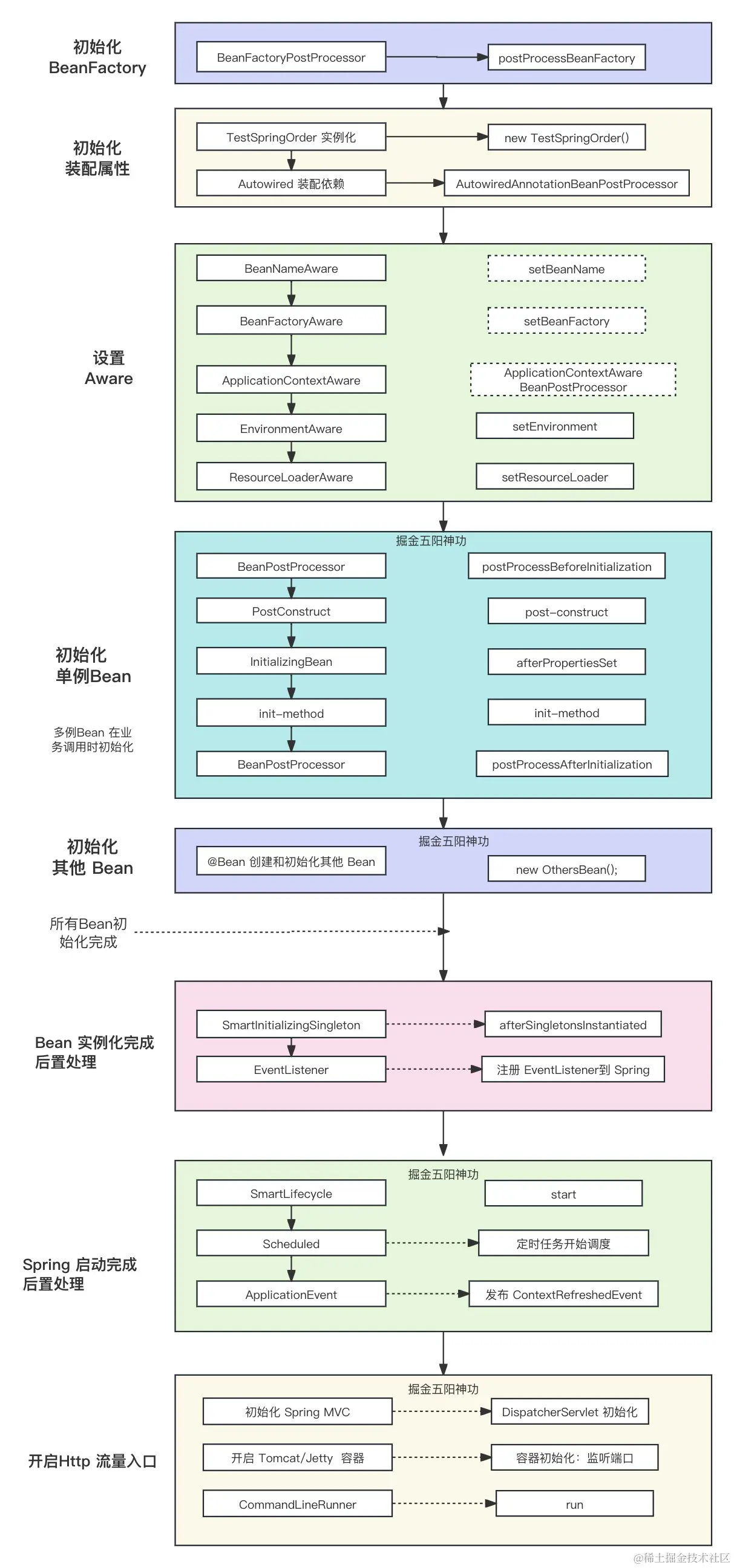
Spring 生命周期相关拓展点
发布
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent这个阶段只能通过
spring.factories或者手动向SpringApplication注册 Listener
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener#starting: 上面的ApplicationStartingEvent发布也是通过这里发出去的, 实现类:org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener实现类需要通过
spring.factories添加进去
发布
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent: 当加载好一些系统环境变量之后, 会发布该事件, 这里有几个重要的 Listener:org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener: 在这个节点初始化日志系统, 所以在这个节点之前使用 log 打印日志一般情况下是不会有输出的, 因为日志系统尚未初始化.如果需要在这个时机之前打印日志, 可以使用 ⭐
DeferredLogFactory实现, 原理是先将日志缓存起来, 待日志系统初始化完成之后, 调用org.springframework.boot.logging.DeferredLogs#switchOverAll进行日志的重放.
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener: 负责加载并调用org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor: 在环境变量准备好之后, 通过EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener处理, 实现类必须通过spring.factories注册. 改接口几个重要的实现类:org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor: 负责加载application.yaml配置文件, 加载逻辑以及顺序封装在了org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentorg.springframework.boot.env.RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor: 负责处理随机变量, 比如${random.uuid},${random.value}等
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener#environmentPrepared上面的
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent是从改节点发布出去的
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize: 用于在ApplicationContext被刷新(refresh)之前对其进行编程初始化。这种机制允许在上下文刷新之前插入一些自定义的逻辑或配置.ApplicationContextInitializer的一个经典实现是PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration, 该实现通过拿到PropertySourceLocator的实现向ConfigurableEnvironment注入外部配置, 比如 Nacos 配置中心就是这么实现的, 参考NacosPropertySourceLocator.
发布
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationContextInitializedEventorg.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener#contextPrepared上面的
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent在该阶段发布
发布
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationPreparedEvent, 该事件几个重要的监听:org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener#onApplicationPreparedEvent将初始化后的日志系统注册到 Spring 容器中org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener#onApplicationPreparedEvent调用缓存日志DeferredLogs#switchOverAll进行日志重放
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener#contextLoaded上面的
ApplicationPreparedEvent在该节点发布
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry在 Bean 初始化之前加载更多的 Bean,BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类, 优先于BeanFactoryPostProcessor加载, 在 Spring 中比较重要的实现:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor: 负责解析配置类, 比如 ⭐@Configuration, ⭐@Import等, 其中@Import涉及的拓展点如下:org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportSelector#selectImports: 返回需要注册成 bean 的类名, 用于基于条件选择并导入配置类, 适用于简单的条件性配置加载, 比如CacheConfigurationImportSelectororg.springframework.context.annotation.DeferredImportSelector:ImportSelector的子类, 在所有 @Configuration的类加载完之后调用, 可以确保某些配置类只有在其他配置类处理完之后才被加载.org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions: 另一个用于在配置阶段注册额外 bean 定义的接口。它提供了更大的灵活性,可以直接操作BeanDefinitionRegistry, 进行跟复杂的 BeanDefinition 配置, 比如ConfigurationPropertiesScanRegistrar
org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean: 严格来说这个接口是 Bean 的一个拓展, 并不是控制 Spring 生命周期的, 这里列出来只是它也算一个拓展点, 用于创建复杂的 Bean, 比如 AOP 相关的.ProxyFactoryBean: 创建AOP代理相关的 Beanorg.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean: 创建 SqlSession Beanorg.apache.dubbo.config.spring.ReferenceBean: 创建 Dubbo@Reference代理 Bean
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory: 实际的 bean 实例化之前,对 bean 的定义(BeanDefinition)进行修改, 这种机制允许我们在容器初始化的早期阶段插入一些自定义的逻辑或配置. 比较经典的实现:org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer: 这是一个常见的实现类,用于解析 ⭐@Value("${foo.bar}")注解中的占位符, 比如。它从外部资源文件(如properties文件)中读取值,并将这些值注入到 Spring bean 中。org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockitoPostProcessor: 处理@MockBean
⭐⭐⭐
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization, postProcessAfterInitialization: 这是关于 Spring 生命周期最重要的接口了, 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean创建 Bean 的逻辑中获取所有 BeanPostProcessor 并 for 循环 apply. 包括它的子类定义了一些列生命周期的回调, 比如实例化之前, 属性注入时, 初始化, 销毁等.ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor: 在初始化之前绑定 ⭐@ConfigurationProperties中的属性.⭐
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation, postProcessAfterInstantiation, postProcessProperties:BeanPostProcessor的子类, 在这基础上添加了实例化之前, 实例化之后, 注入属性后的回调.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 负责处理 ⭐@Autowired以及@Value值的注入.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor: 新增了暴露早期引用getEarlyBeanReference方法用于解决循环依赖问题, 有关 AOP 以及代理相关的操作大部分来源于该接口的实现类, 比如@Async,@TransationalAsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理 ⭐@Async方法, 包装成代理实现异步
ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 负责注入@DubboReference字段
org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor: 初始化之前注入实现了 *Aware 的相关资源, 比如ApplicationContextAware,EnvironmentAware等, 但除了BeanNameAware,BeanClassLoaderAware以及BeanFactoryAware, 这三个比较特殊, 是在初始化之前在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeAwareMethods进行处理的.EmbeddedValueResolverAwareResourceLoaderAwareApplicationEventPublisherAwareMessageSourceAwareApplicationStartupAwareEnvironmentAware⭐
ApplicationContextAware
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor: 定义了销毁前的 callbackInitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 负责处理 ⭐@PostConstruct以及 ⭐@PreDestroy, 因为是在BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization中处理的, 加载时机在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods(回调 ⭐InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet以及@Bean中指定的 ⭐initMethod) 之前CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理 ⭐@Resource注解
ApplicationListenerDetector: 将 ⭐ApplicationListener的实现类放到ApplicationEvent的监听列表中ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理 ⭐@Scheduled注解
org.springframework.beans.factory.SmartInitializingSingleton#afterSingletonsInstantiated: 在所有单例 bean 都初始化完成之后执行一些特定的逻辑.EventListenerMethodProcessor: 处理 ⭐@EventListener注解.
⭐
org.springframework.context.SmartLifecycle#start: 主要用于需要在应用程序启动和停止时执行特定操作的组件, 是用于开启流量类的操作, 比如启动 Web 容器, 启动 MQ 监听, 启动定时任务等, 下面是一些实现类:WebServerStartStopLifecycle: 启动 Web 容器, 并发布ServletWebServerInitializedEvent事件.RedisMessageListenerContainer: 启动 Redis 事件订阅SchedulerFactoryBean: 启动 Quartz 定时任务NacosWatch: 监听 Nacos 配置变化
发布
org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent事件以前的
DispatcherServlet就是通过该事件进行初始化的.DubboBootstrapApplicationListener启动 Dubbo (DubboBootstrap#start)
发布
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEventTomcatMetricsBinder: 监听ApplicationStartedEvent启动, 绑定TomcatMetrics到MeterRegistry.
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener#started上面的
ApplicationStartedEvent通过该节点发布
org.springframework.boot.Runner, 该接口有两个实现org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner#runJobLauncherApplicationRunner: 启动 Spring Batch Job
org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner#run
发布
org.springframework.boot.context.event.SpringApplicationEventBackgroundPreinitializer: 对于一些异步初始化的任务, 在这里 await 等待所有任务执行完毕.
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener#readySpringApplicationEvent在这里发布
到此为止, 启动相关的拓展点基本就这些了, 接下来是销毁阶段的一些接口:
org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEventDubboBootstrapApplicationListener: 调用 Dubbo 相关 shutdown hook
⭐
org.springframework.context.Lifecycle#stop: 容器销毁前回调ExecutorLifecycleDelegate: 关闭线程池WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle: 优雅关机
Spring Bean PreDestroy
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeDestruction:SimpleServletPostProcessor: 销毁 ServletInitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理 ⭐@PreDestroy注解
⭐
org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean#destroyOkHttp3ClientHttpRequestFactory: 关闭线程池RedissonConnectionFactory: 关闭 Redisson 连接池
@Bean(destroyMethod = "destroyMethod")java.lang.AutoCloseable: 只有当上面三个销毁方式都没有定义时, 才会触发该接口
Spring Boot Starter 的推荐实现方式
Starter 标准的实现姿势在 Spring Boot 自身的包中就已经有很多参考了.
声明配置类, 并在类上贴
@AutoConfiguration(2.7.0 以前的版本使用@Configuration)注解, Bean 在配置类中声明在
spring.factories或者org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports(Spring Boot 3.0 之后的方式) 加上配置类
Example:
@AutoConfiguration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RabbitProperties.class)
public class MyAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MyAbility myAbility() {
return new MyAbility();
}
}
public class MyAbility {
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello World!";
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.example.autoconfig.MyAutoConfiguration如果是 Spring Boot 3.0+, 则需要声明在 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
com.example.autoconfig.MyAutoConfiguration注意点
对于配置 Properties 类, 尽量使用 @ConfigurationProperties + @EnableConfigurationProperties 使用.
Ref
- 0
- 0
-
赞助
 微信
微信
-
分享